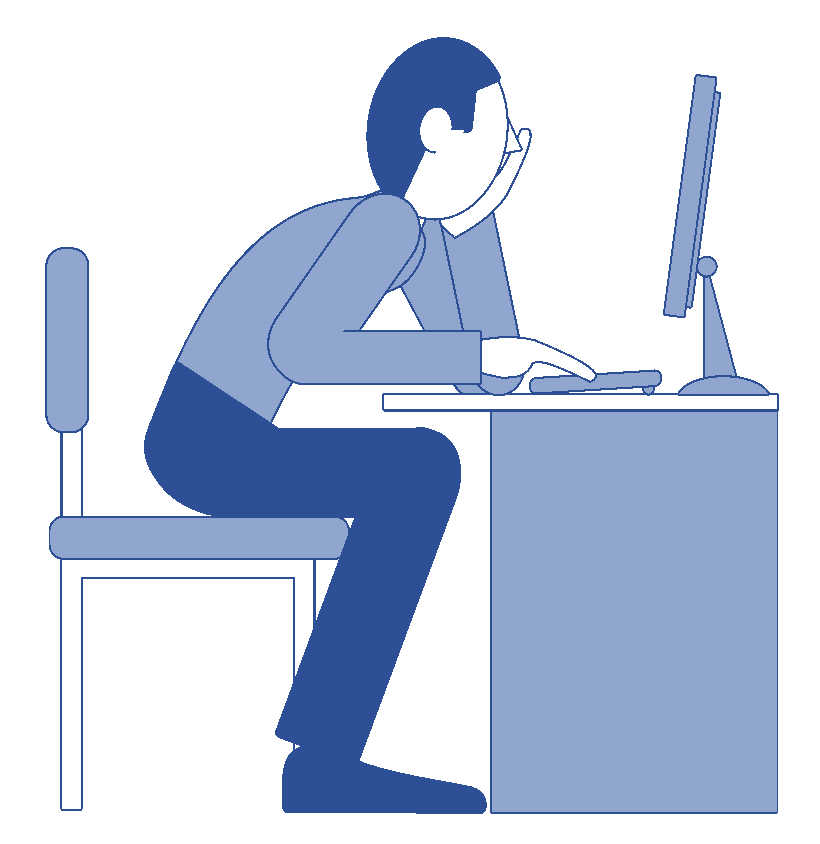
Why DSE safety matters
Sitting at a screen for extended periods can lead to:
But these health risks are preventable. By following ergonomic principles, you can improve your workplace health and reduce the risk of injury.
How to sit properly at a desk with a computer?
To avoid neck strain, eye strain, and back pain, your posture and workstation setup are key. Some key points to remember:
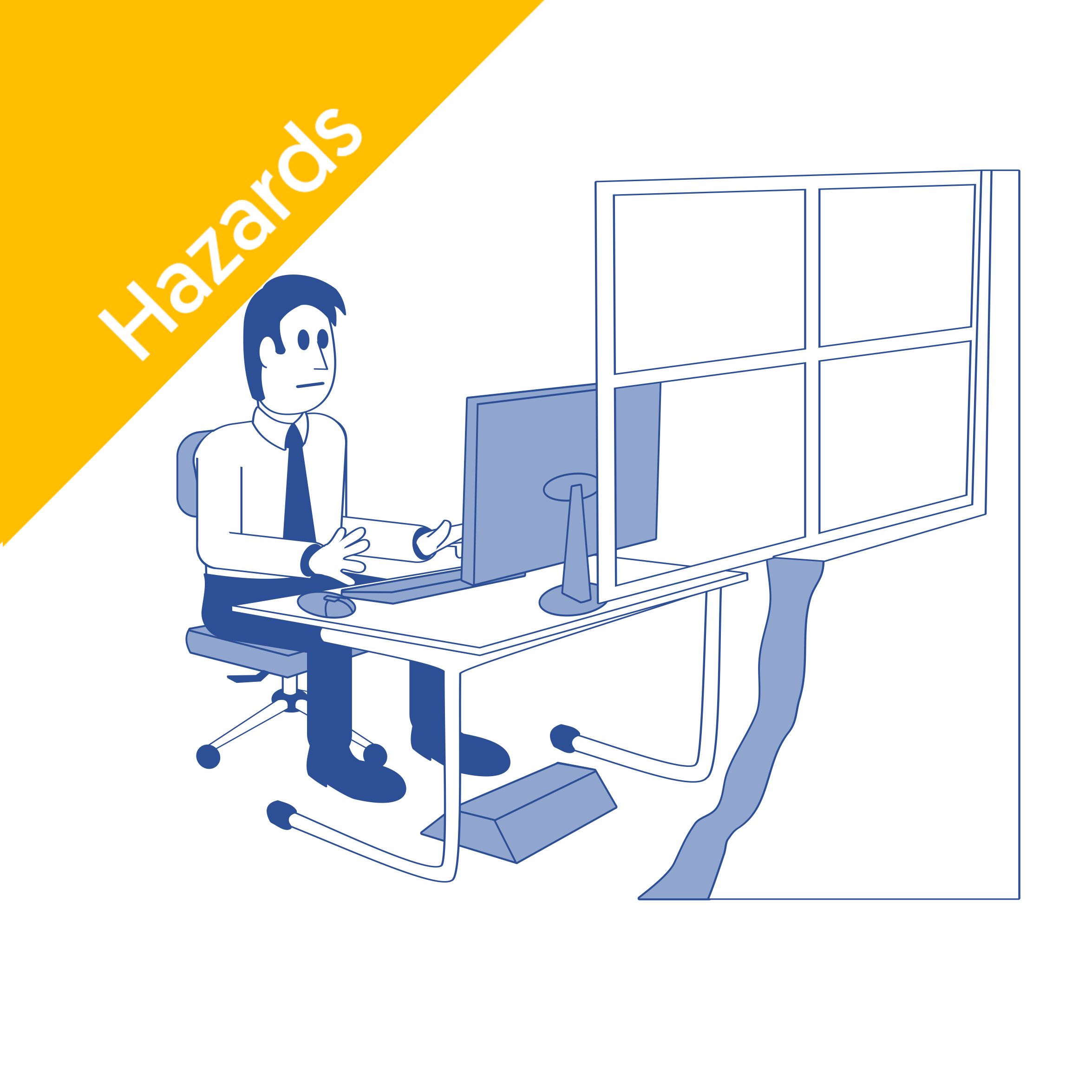
Workstation setup for safe use of DSE
Following a workstation checklist is the first step toward comfort and safety. Here’s what to look for:
Proper posture:
Sit upright with proper alignment
Support the lower back with the back of the chair
Relax your shoulders and keep your elbows close to your sides
Monitor and screen:
Keyboard and mouse:
Keep wrists straight and hands level
Use a keyboard that allows relaxed typing
Position the mouse within easy reach, avoiding overextension
Work surface:
Take breaks and vary your posture
Staying still for too long, even in the “right” position, can still cause discomfort. Regular movement is essential for circulation, concentration, and occupational safety.
Tips:
Take frequent breaks — aim for 5–10 minutes every hour
Stand, stretch, or walk around to boost blood flow
Change your seated position throughout the day
Protect your eyes from screen fatigue
Eye strain is a common side effect of long periods of screen work. You can reduce the risk by:
Following the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 meters away for 20 seconds
Adjusting screen brightness and contrast
Reducing glare from lights or windows
Keeping screens clean and readable
DSE risk assessment: what should you do?
All employees who use screens regularly should have access to a DSE risk assessment. This checks your workstation setup, identifies control measures to improve safety, and ensures records of risk assessments are kept up to date.
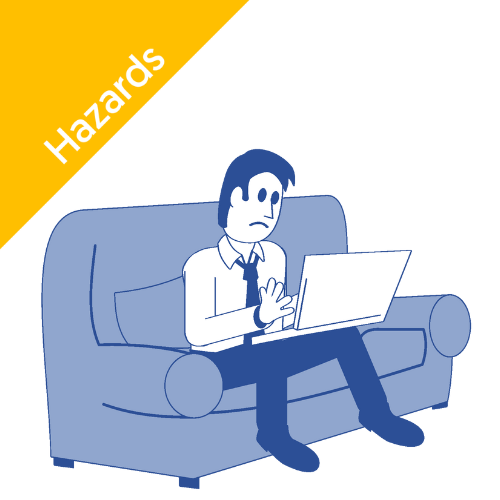
If your work environment changes — such as switching desks or working from home — your employer may need to reassess your setup.
For tips on a safe working-from-home setup, check out this Knowledge Bank article.
Check out our step-by-step guide on conducting a risk assessment for your workstation.
Can you request an eye test?
Yes. In the UK, if you're a screen user, your employer must provide you with an eye test on request and contribute to the cost of corrective lenses if needed for screen work. This is part of their legal obligations under the DSE regulations.
DSE user responsibilities
While your employer is responsible for assessments and providing equipment, you also have responsibilities. As a DSE user, you should:
Follow training on the safe use of display screen equipment
Report any discomfort or health issues promptly
Use equipment correctly and make necessary adjustments
Maintain good posture and take breaks to reduce strain
Looking after your mental health
Physical discomfort can affect your mood and concentration, and chronic pain may even lead to burnout. Make sure you:
Take screen breaks away from your desk
Adjust your workload where possible to avoid fatigue
Raise concerns about health risks or workplace health with your manager or HR team
Final thoughts
By understanding your role as a screen user, setting up your workstation correctly, and building healthy work habits, you can reduce discomfort and help prevent musculoskeletal problems, eye strain, and other injuries related to incorrect use of screens and monitors.
For extra support, many workplaces offer access to a specialist training course to guide you through best practices. If you're unsure what your responsibilities are, ask your employer or consult the HSE website for more on DSE risk assessments and safe screen use.
Further Reading

DSE
What do the display screen equipment regulations require users to do? Explore insights on VDU equipment and health & safety requirements in our guide.

DSE
What do the display screen equipment regulations require users to do? Explore insights on VDU equipment and health & safety requirements in our guide.

DSE
Discover the essentials of DSE working from home in our comprehensive guide. Learn tips and best practices to optimise your remote work experience!

DSE
Learn how to conduct a thorough risk assessment for display screen equipment. Protect your health and optimise workplace safety with our comprehensive guide.

DSE
What do the display screen equipment regulations require users to do? Explore insights on VDU equipment and health & safety requirements in our guide.

DSE
What do the display screen equipment regulations require users to do? Explore insights on VDU equipment and health & safety requirements in our guide.

DSE
Discover the essentials of DSE working from home in our comprehensive guide. Learn tips and best practices to optimise your remote work experience!

DSE
Learn how to conduct a thorough risk assessment for display screen equipment. Protect your health and optimise workplace safety with our comprehensive guide.